
What are Sitemaps in SEO & Why Your Website Needs One?

What is a Sitemap?
A sitemap is a file that contains details about the pages, videos, and other files on your website, as well as their interconnections. Search engines such as Google use this file to crawl your site more effectively. A sitemap can be very beneficial for SEO purposes as it allows Google to find and index important pages on your site more easily. This is especially crucial for websites that are larger, have a vast amount of archived content, or use rich media content. Using a sitemap for Google SEO ensures that search engines can more efficiently process the content of your site, potentially boosting your rankings by helping Google’s crawlers navigate your site’s structure and prioritize the indexing of new or updated content.
Types of Sitemaps in SEO
Normal XML Sitemap: This is the most prevalent type of sitemap, typically formatted as an XML Sitemap that connects to various pages on your website.
Video Sitemap: Specifically designed to assist Google in recognizing video content on your page.
News Sitemap: Facilitates Google’s discovery of content on websites that are certified for Google News.
Image Sitemap: Aids Google in locating all the images hosted on your site.
XML Sitemap
An XML Sitemap is an essential tool for websites, serving as a digital map that guides search engines through all the significant pages available for crawling. This structured file provides search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo detailed insights into the website structure, ensuring that they can discover and index the site’s content more efficiently.
Structured in XML (eXtensible Markup Language), this type of sitemap lists URLs along with crucial metadata for each link—such as the last modification date, the frequency of changes, and the priority of the page in relation to other pages. This information helps search engines prioritize their crawling according to the sitemap’s instructions, which is particularly beneficial for large websites or those that frequently update their content.
Integrating an XML Sitemap into your website is a powerful Sitemap SEO strategy. It not only enhances the visibility of your pages in search engine results but also ensures that newly added content is indexed quickly. For website administrators, an XML Sitemap is a proactive approach to inform search engines explicitly about all the pages that should be considered for indexing, thereby optimizing the website’s search engine performance and visibility.
HTML
An HTML sitemap is a webpage that lists all important pages of a website in a structured manner, making it easier for users to navigate and find content on the site. Unlike XML sitemaps, which are intended for search engines, HTML sitemaps are designed with the user experience in mind. They provide a clear and simple overview of a website’s layout, offering links to various sections and pages in an organized format.
Including an HTML sitemap on your website can significantly improve user experience by enabling visitors to quickly locate the information they need. This is particularly beneficial for websites with a large number of pages or complex structures. By helping users navigate your website more efficiently, an HTML sitemap can reduce bounce rates and increase the time spent on the site, which are important factors in SEO.
Furthermore, an HTML sitemap can also aid in SEO (Sitemap SEO) by ensuring that search engines can crawl all accessible pages, boosting the visibility of older articles or those buried deep within the site. This dual functionality makes HTML sitemaps a valuable tool for both improving user experience and enhancing search engine optimization.
Tips for Optimizing Sitemaps
Optimizing sitemaps is a crucial task for enhancing your website’s search engine optimization (SEO). A well-optimized sitemap can make your site more visible and comprehensible to search engines, helping to improve indexing efficiency and accuracy. Here are some tips for optimizing your sitemaps effectively:
1. Keep Your Sitemap Updated
Regularly update your sitemap to include new pages and remove any that have been deleted. An up-to-date sitemap ensures that search engines are aware of all the current pages on your site, which helps to improve the indexing of new content. Implement automatic updates if your website’s content changes frequently.
2. Prioritize Important Pages
In your XML sitemap, you can set the priority of each URL to signal to search engines which pages are most important. Use the <priority> tag to differentiate between high-priority pages (like your homepage or main product pages) and lower-priority pages. This helps search engines understand which content you deem most valuable, influencing crawl frequency.
3. Use Last Modified Field
The <lastmod> field in your XML sitemap tells search engines the last time a page was updated. Accurate use of this field can prompt search engines to re-crawl updated pages, ensuring that the content in search results is current. This is particularly important for sites with regularly updated content, like news portals or blogs.
4. Limit the Number of URLs
To ensure optimal processing by search engines, keep each XML sitemap file limited to 50,000 URLs or stay under the file size limit of 50MB. If your site has more URLs, split them into multiple sitemap files and link them through a sitemap index file. This division helps prevent any single sitemap from becoming too large, which can hinder its processing by search engines.
5. Categorize Sitemaps
For large websites, categorizing sitemaps can be incredibly effective. For instance, you can have separate sitemaps for blog posts, products, categories, and more. This organization makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site based on content types and relevance, enhancing the overall SEO strategy.
6. Include Only Canonical URLs
To prevent duplicate content issues, ensure that your sitemap contains only canonical URLs. This prevents search engines from indexing multiple versions of the same page. It’s crucial for maintaining the integrity of your SEO efforts and ensuring that the right pages rank in search results.
7. Use Responsive URLs for Mobile-First Indexing
With mobile-first indexing, Google primarily utilizes the mobile version of content for both indexing and ranking purposes.
Ensure your sitemap includes mobile-friendly URLs, especially if you have separate URLs for mobile and desktop versions. This alignment with Google’s mobile-first approach is vital for maintaining visibility in mobile search results.
8. Validate Your Sitemap
Regularly check your sitemap for errors using tools like Google Search Console. This tool can help you identify and fix issues such as broken links, incorrect formats, or URLs blocked by robots.txt. Validation ensures that your sitemap remains effective and free from errors that could negatively impact your SEO.
9. Submit Your Sitemap to Search Engines
Don’t assume search engines will automatically find your sitemap. Manually submit it through Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to ensure it’s recognized and processed. This submission notifies search engines of its existence and aids quicker indexing.
10. Monitor Sitemap Statistics
After submission, monitor your sitemap’s performance through Google Search Console. Check how many pages are indexed versus submitted, identify any crawl errors, and observe how updates to your sitemap impact your site’s indexing. This ongoing monitoring can provide insights into your SEO strategy’s effectiveness and areas for improvement.
Following these tips can significantly enhance the efficiency with which search engines index and understand your website, thereby improving your site’s overall SEO performance. Optimizing your sitemap is not just about making it available to search engines, but ensuring it effectively communicates your site’s structure and content priorities.
How to Find the Sitemap of a Website?
Here are some practical methods to find a sitemap on a website:
Manual Check
First Open Google or any Search Engine and Write this text for Google search.
https://domain.com/sitemap.xml
https://digitalretina.in/sitemap.xml
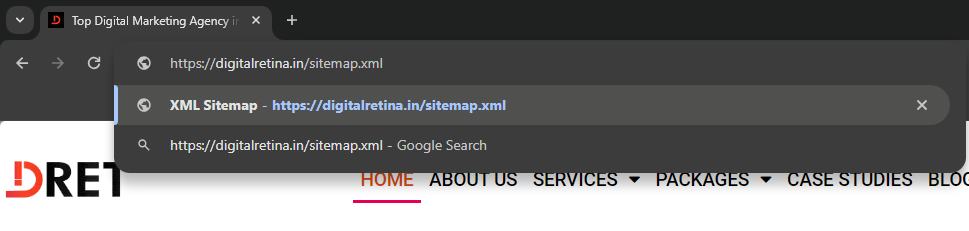
Then
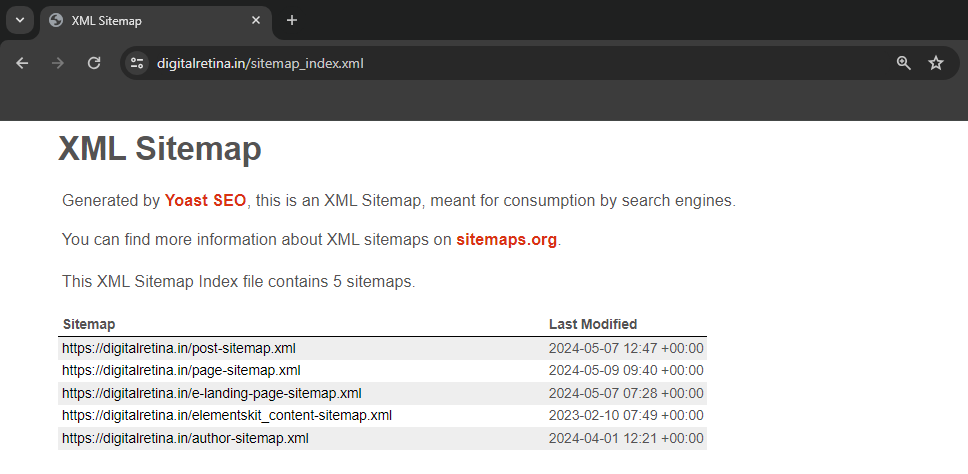
As you may notice, a sitemap index is a straightforward file that enumerates all the sitemaps of a website. (Indeed, there can be multiple sitemaps.)
To view the actual sitemap, simply click the link to the specific sitemap listed in the index.
Google Search Console
If you can access a website’s Google Search Console, you might find the sitemap submitted there.
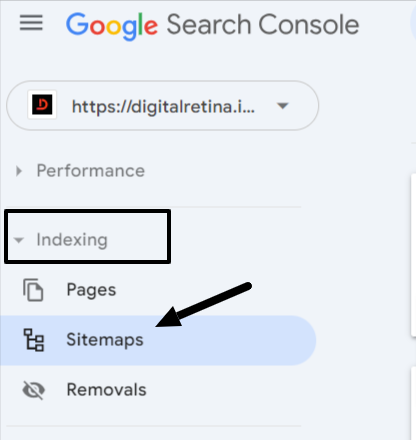
In this section, labeled “Submitted sitemaps,” you can see if an XML sitemap has previously been submitted. If it has, the URL of the sitemap will be listed here.
In conclusion
Effectively managing your sitemap is a cornerstone of successful Sitemap SEO. A well-organized and regularly updated sitemap for a website not only helps search engines crawl your site more effectively, but also ensures that all your important pages are indexed. By adhering to best practices for sitemap optimization, you can enhance your website’s visibility and improve its overall searchability. Remember, a sitemap is more than just a technical necessity; it is a strategic tool that can significantly impact your website’s performance in search results. By prioritizing the management of your sitemap, you are setting a solid foundation for your website’s SEO success.
Take your website’s SEO to the next level with our expert services. Contact the leading SEO Company in Noida today and let us help you optimize your sitemap for maximum results!
digitalretina
Jayant Singh
Meet Jayant Singh, the visionary CEO of Digital Retina. With over 8 years of expertise in digital marketing and brand growth strategies, Jayant's leadership has led to the successful transformation of numerous businesses. His knack for innovative solutions continues to shape the digital marketing landscape.


Comprehensive Guide to PPC Strategies: How to Make the Most of Your Paid Advertising

